|
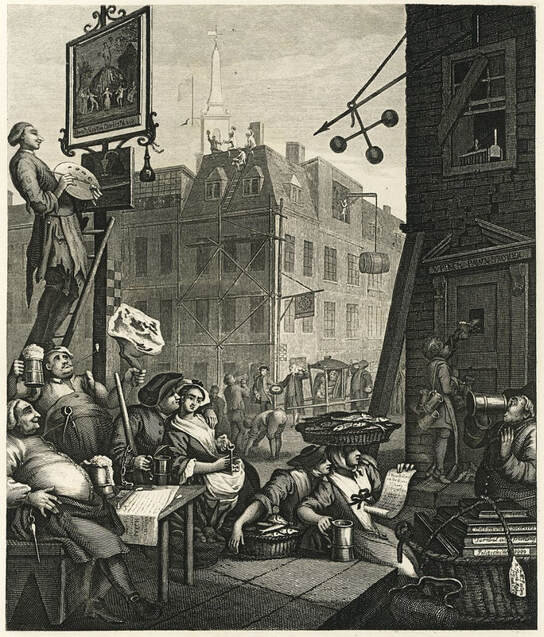
Where? Room 1730 of the Main Floor of Tate Britain. Several other museums like the British Museum, Metropolitan Museum of Art, and National Gallery of Art also own this work but do not have it on permanent display.
When? 1751 What do you see? Several groups of well-fed people engage in a variety of activities while drinking mugs of beer. It is the birthday of King George II, and that asks for a celebration. On the left, two corpulent men hold big mugs of beer and one of them holds a huge leg of beef in his left hand. In front of them sits a man holding a beer while sharing a romantic moment with a woman. To the right of them, a couple of women with overflowing baskets of fish pause while enjoying a beer. To their right, a young boy with mugs hanging on a rope slung over his back goes around selling mugs of beer. He stops at the pawnbroker to hand him a beer through the peek hole. The pawn shop is in some state of disrepair as people do not need to pawn off their belonging in this prosperous world where people drink beer. The other buildings are well-maintained, and the church steeple on the top is a sign that people behave morally in this world full of beer. On the bottom right, a portly man enjoys his beer next to a pile of books in a basket. On the left, a painter in ragged clothes blissfully paints a cheery picture of men and women dancing around a mountain of barley. On top of the roofs, construction workers take a break drinking to celebrate while another barrel of beer is being lifted up. Finally, in the center, a wealthy woman in a sedan chair waits as her chairmen have temporarily put her chair down to drink a beer. Laborers around them drink their beer while continuing their work in a timely manner. Backstory: Beer Street takes place during a major movement in 18th-century England: The Age of Enlightenment. This was a philosophical and intellectual movement where people began to ponder major scientific and philosophical thoughts that were captured in paintings such as The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp by Rembrandt. These ideas were published, and many people learned from them and developed them further. Another idea behind the Age of Enlightenment is that people were trying to apply these new ideas to help other people. Before the Gin Craze, French brandy was popular and fashionable, however, during the Second Hundred Years’ War between France and England, French products were considered unpatriotic and soon lost their following. This led to the Gin Craze where gin and other cheap spirits quickly became popular, and overconsumption of these drinks caused many problems among the lower-class people. William Hogarth’s print was, in essence, a piece of propaganda in favor of the British beer market. Similar to the popularity of Coca-Cola in the United States during modern times, Hogarth makes the argument that beer was not only a remedy to the unregulated gin trade but also a drink that is truly British and helps the country.
Gin Lane: At the time Hogarth created Beer Street, he also created a companion piece called Gin Lane. Most museums that own Beer Street, also have a print from Gin Lane as they were created together. Museums owning Gin Lane include Tate Britain, the British Museum and the National Gallery of Art. However, most museums do not have the prints on permanent display as they are light sensitive. The original copperplates for both works are owned by the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Gin Lane shows the perilous effects that excessive gin consumption can have on your life. It shows the opposite side of Beer Street where drinking gin leads to chaos, negligence, street brawls, and poverty. The only ones benefiting from the gin craze are the distillery, the pawn shop, and the undertaker.
Who is Hogarth? William Hogarth was born in 1697 in London where he would die 66 years later. Hogarth carefully examined life in 18th-century London and detailed it in etchings and painted satires. He included many symbolic features in his works such that his pieces are not only entertaining but also contain several moral messages.
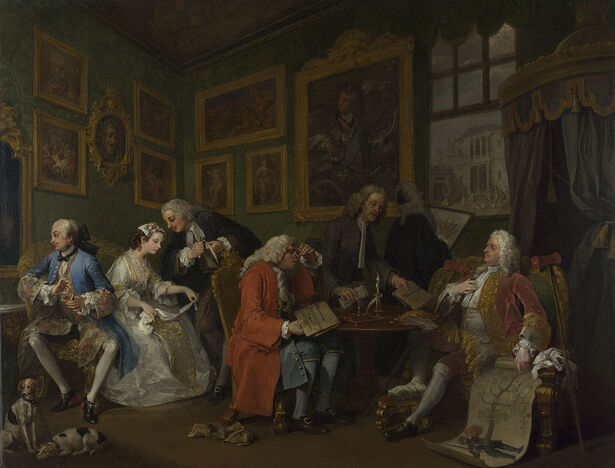
Hogarth created art both for the upper and lower class. He painted works for his richer clients but also created etchings and engravings of his works that could be mass-produced and sold at a lower price to a larger audience. Among his works is a series of satirical works about the British upper class. The first painting of that series is Marriage A-la-Mode: 1, The Marriage Settlement in the National Gallery in London.
0 Comments
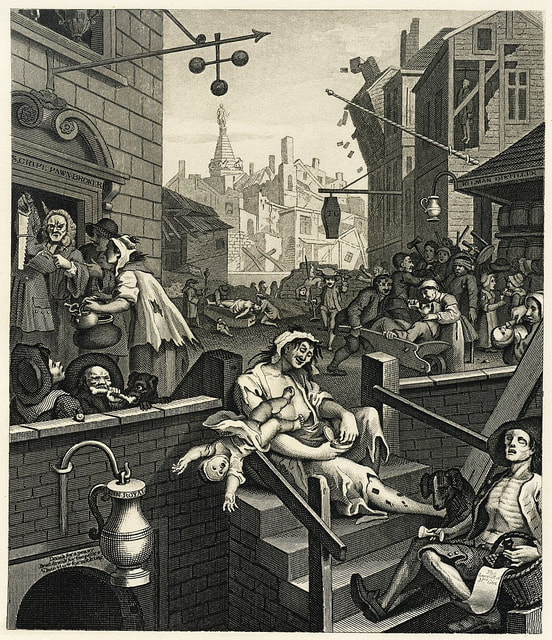
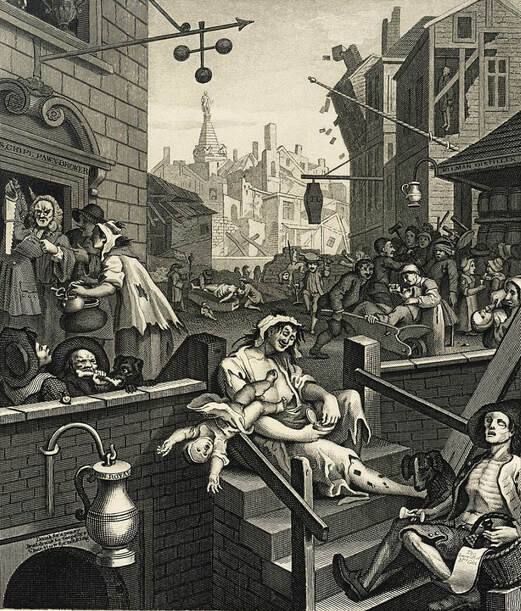
Where? Room 1730 of the Main Floor of Tate Britain. Several other museums like the British Museum, Metropolitan Museum of Art, and National Gallery of Art also own this work but do not have it on permanent display.
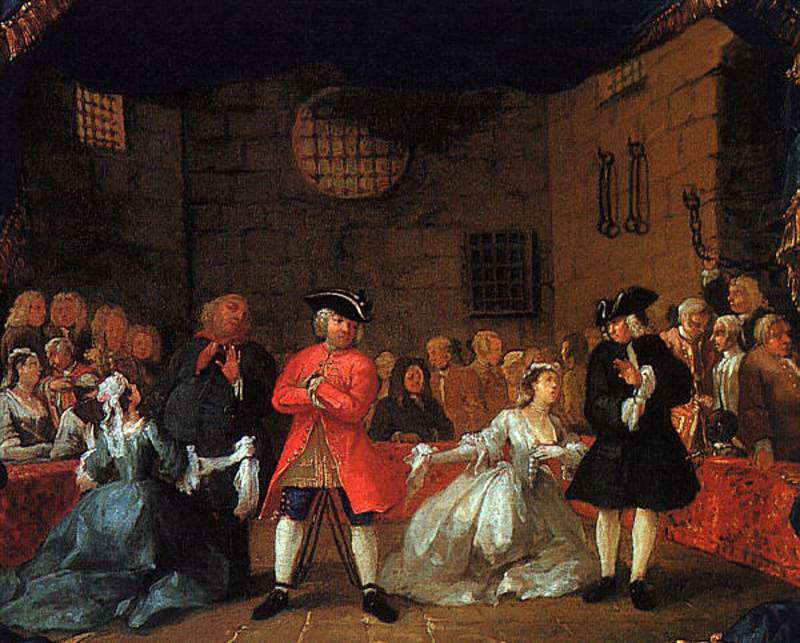
When? 1751 What do you see? People in various states of physical and mental decline amid a chaotic urban setting. In the center sits a woman with ragged clothes. Her shirt is open exposing her breasts, and she has sores on her legs. She neglects her baby who falls out of her arms and does not even notice what is happening. Just down the steps from her lies a malnourished soldier who looks like a skeleton. He has his head tilted back and holds on to an empty glass of gin. A dog with a saddened expression looks over him. The soldier has a basket tucked under the crook of his arm with a bottle and note that reads “The Downfall of Gin.” To the left of the central woman, two men fight with a dog over a bone signifying how far they have fallen because of their gin addiction. Standing above them, a couple of men try to pawn off possessions to buy more gin. On the right side, more people lose themselves to the cheap spirits. People are feeding gin to each other, including children, and even a baby. In front of the distillery on the right middle, a fight breaks out and people hit each other with chairs and hammers. There is a strong contrast between the different buildings in this town. Most buildings in the background are in poor condition, except the distillery, the pawn shop, and the undertaker’s building. Backstory: Gin Lane is an etching and engraving printed on paper. Hogarth chose this technique to be able to produce multiple prints of his work that he could sell for low prices to lower-class people. Gin Lane showcases the vicious cycle of excessive drinking, pawning off your possessions to drink more, prostitution, and finally death. Gin drinking was considered a large problem in England during the time that Hogarth created this work. It was cheap and accessible to the working class, and many people got addicted to gin with all the bad consequences that result from that. Gin Craze: In the beginning of the 18th century, gin was not regulated in England, and distillers did not care much about the drink’s quality. They mixed in harmful chemicals and did anything to increase their margins. The drink became very popular among the lower class in England, and especially in London. Many people consumed large quantities of gin, which made them even poorer and led to health problems. The problems with gin led the government to take several measures between 1729 and 1751 to make gin more expensive and reduce its popularity. These measures only had a partial effect, and it was not until the 1750s that the gin consumption decreased mainly due to a series of poor grain harvests. Beer Street: At the time Hogarth created Gin Lane, he also created a companion piece called Beer Street. Prints of this work are part of multiple collections, including the British Museum and the National Gallery of Art. The original copperplates for both works are owned by the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Beer Street presents an alternative to the ails of gin drinking. It shows the opposite of the street where we see that beer drinking leads to prosperity. It shows a town that is flourishing with healthy individuals engaging in fun activities. For example, the pawnbroker that thrived in the chaos in Gin Lane is in disrepair as no one wants to pawn items to support their habit.
Who is Hogarth? William Hogarth was born in 1697 in London where he would die 66 years later. He enjoyed creating art which explains the social ills of 18th-century England through a combination of wit and symbols that would be easy to understand for his 18th-century audience. He created art both for the upper and lower class.
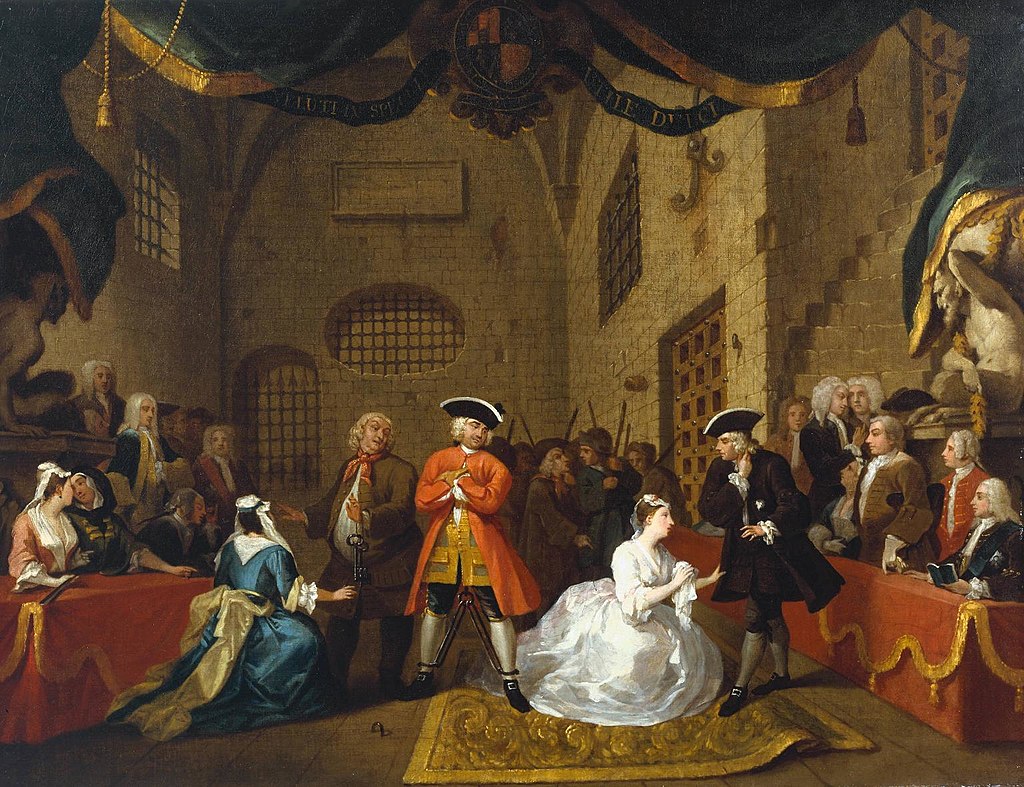
Hogarth painted works for his richer clients but also created etchings and engravings of his works that could be mass-produced and sold at a lower price to a larger audience. An example of a work for the upper class is A Scene from 'The Beggar's Opera' in the National Gallery of Art. Another version of this painting is in the same room as Gin Lane in Tate Britain.
Fun Fact: In addition to being a political satirist, William Hogarth is known for his caricatures of people. Look, for example, at the man hanging from the rafters in the top right of Gin Lane or the man in the center walking down the street with a baby on a stake.
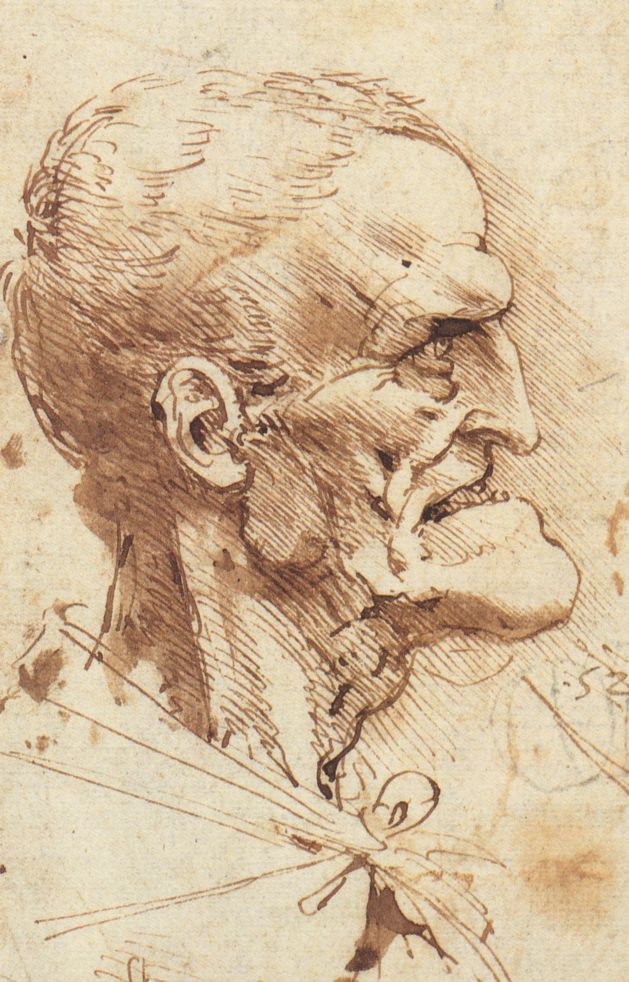
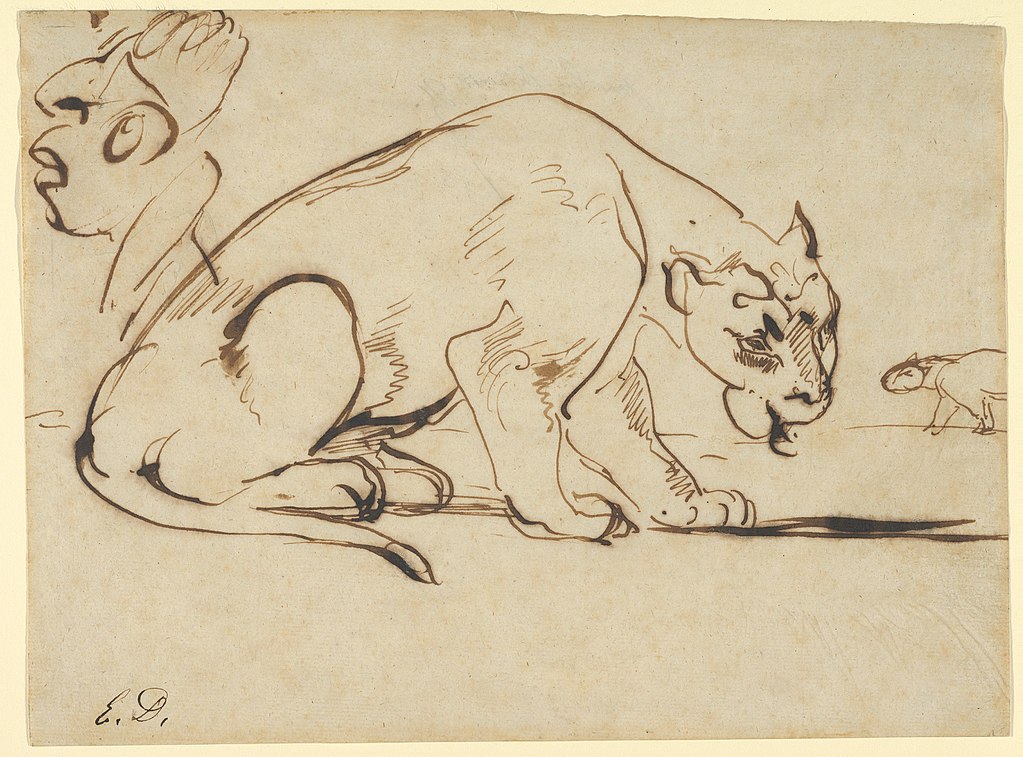
Other artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Eugene Delacroix also liked to create caricatures of people. One of Da Vinci’s many caricatures is a drawing of a Grotesque Profile. An example of a caricature by Delacroix is A Lioness and a Caricature of Ingres in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. |
Categories
All
|
- Home
- Blog
-
Museums
- Alte Pinakothek
- Art Institute of Chicago
- Baltimore Museum of Art
- Barber Institute of Fine Arts
- Bargello
- Barnes Foundation
- British Museum
- Church of Sant’Anastasia
- Cleveland Museum of Art
- Courtauld Institute of Art
- Detroit Institute of Arts
- Frans Hals Museum
- Galleria Borghese
- Gallerie dell'Accademia
- Getty Museum
- Guggenheim
- Hermitage Museum
- Kunsthistorisches Museum
- Kunstmuseum Basel
- Legion of Honor Museum
- Louvre
- Mauritshuis
- Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Musee d’Orsay
- Museum of Fine Arts in Boston
- Museum of Modern Art
- National Gallery in London
- National Gallery of Art
- National Museum in Poznań
- Norton Simon Museum
- Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek
- Palace of Versailles
- Palazzo Pitti
- Palazzo Vecchio
- Petit Palais
- Philadelphia Museum of Art
- Prado
- Pushkin Museum
- Ravenna Art Museum
- Rijksmuseum
- San Diego Museum of Art
- Santa Maria delle Grazie
- St. Peter's Basilica
- Städel Museum
- Statens Museum for Kunst
- Tate Britain
- Tate Modern
- Timken Museum of Art
- Uffizi
- Vatican Museums
- Wallace Collection
-
Artists
- Altdorfer
- Anguissola
- Berlin Painter
- Bosch
- Botticelli
- Boucher
- Bronzino
- Bruegel the Elder
- Brunelleschi
- Cabanel
- Caillebotte
- Canova
- Caravaggio
- Carpeaux
- Cezanne
- Cimabue
- David
- Degas
- Delacroix
- De Maria
- Donatello
- El Greco
- Fontana
- Fra Angelico
- Fragonard
- Gauguin
- Gentileschi
- Gericault
- Gonzalez-Torres
- Goya
- Hals
- Hogarth
- Hokusai
- Ingres
- Leonardo da Vinci
- Lippi, Filippo
- Longhi, Barbara
- Lorrain
- Makovsky
- Manet
- Massys
- Matisse
- Merian
- Michelangelo
- Mochi
- Modigliani
- Monet
- Panini
- Parmigianino
- Perugino
- Picasso
- Pisanello
- Raphael
- Rembrandt
- Renoir
- Reynolds
- Rivera
- Rodin
- Rubens
- Scultori
- Seurat
- Steen
- Tintoretto
- Titian
- Toulouse-Lautrec
- Turner
- Uccello
- Van der Weyden
- Van Dyck
- Van Eyck
- Van Gogh
- Van Hemessen
- Vasari
- Velazquez
- Vermeer
- Veronese
- Vigée Le Brun
-
Locations
- Books
- About Us