|
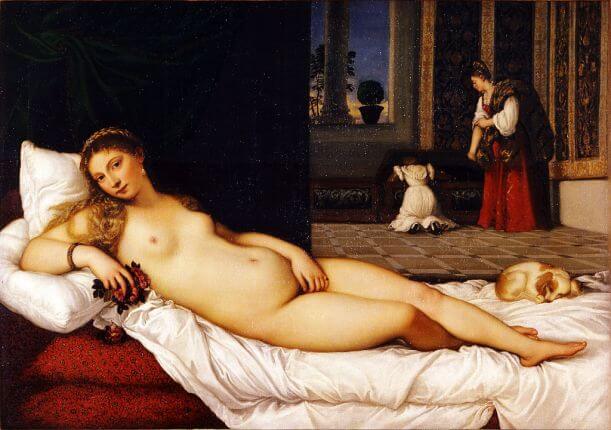
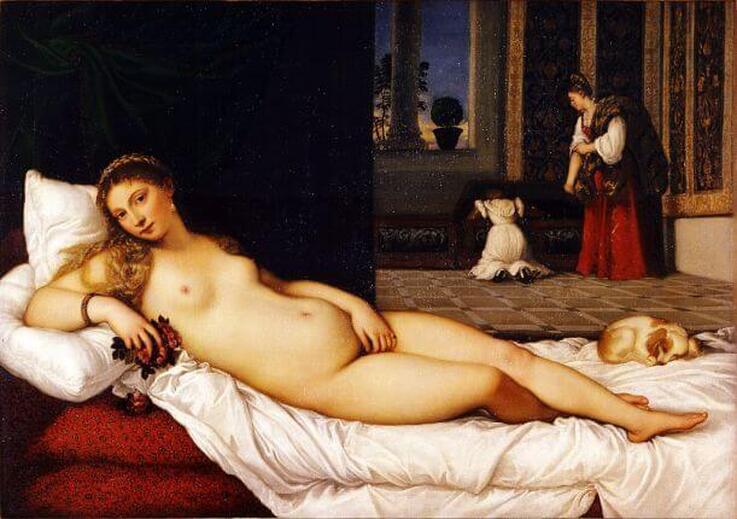
Where? Room 2 of the Musée d’Orsay
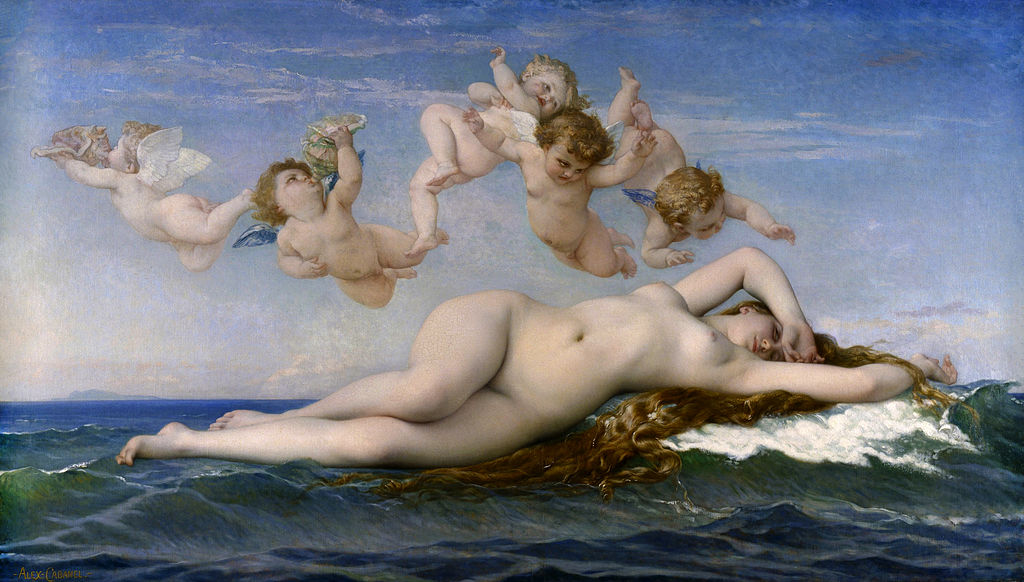
When? 1863 What do you see? A beautiful Venus is born from the foam of the sea. It looks as if she has just awakened from a deep slumber. She languidly rests her head upon a small wave that is beginning to form on the far right. The waters seem to conform to her twisted contrapposto, perfectly following the shape of her waist. Upon first glance, her eyes are shut. But a closer look reveals that they are half-open, pointed upwards as she looks into the crook of her right elbow. Her golden hair flows from beneath her left arm, floating beside her in the blue-green waters. Above her is a pastel sky decorated with thin clouds and five cherubs that are celebrating and announcing her arrival with horns made of seashells. The three cherubs closest to her face peer over her body with playful curiosity, arms stretched out, perhaps preparing to wake her. Backstory: Alexandre Cabanel exhibited The Birth of Venus in the Paris Salon in 1863 in a “Salon of Venuses”. During this time, many artists were painting female nudes shrouded in the mythology of the birth of Venus. The European idealized female nude, a tradition that traces back to the Venus of Urbino by Titian, was experiencing a revival in the 19th century in works like Cabanel’s, as well as the Grande Odalisque by Ingres, and the Maja Desnuda by Goya. The mysticism of the story gave artists room to produce semi-erotic works without offending the public. Cabanel’s Venus is posed in a much more provocative way than Olympia by Manet, but because of Manet’s more realistic and confrontational take on his nude, he received a great deal of criticism in the same year.
What is contrapposto? Contrapposto is a pose that was developed by the Greeks. In contrapposto, the figure rests its weight on one leg and bends the other. The axis of the shoulders and the hips are positioned in opposite directions to create a sense of dynamism and depth. This creates a natural resting pose that makes the figure come alive.
Who is Alexandre Cabanel? Alexandre Cabanel was a French painter born in 1823 in Montpellier, in the south of France. When he was seventeen years old, he enrolled in the Ecolé des Beaux-Artes in Paris. Following his first exhibition in 1844, Cabanel was awarded the Prix de Rome. His work was quickly popularized at the Paris Salon. Cabanel primarily painted in the Academic style and drew inspiration from the Rococo art movement. His works centered around classical, religious, and historical themes. The Birth of Venus, his most famous painting, was exhibited at the Paris Salon and later purchased by Napoleon III. In his later life, Cabanel served as a juror for the Salon and returned to the Ecolé des Beaux-Artes as a teacher. He died in Paris in 1889 at the age of 65. Fun fact: Following the creation of the original, Alexandre Cabanel sold reproduction rights to Adolphe Goupil, an art dealer and publisher. Working with copyist Adolphe Jourdan, Cabanel was able to produce numerous replicas of his take on The Birth of Venus. One of these replicas is on display in the Dahesh Museum in New York. Another one belongs to the Metropolitan Museum of Art but is not on permanent display.
0 Comments
Where?
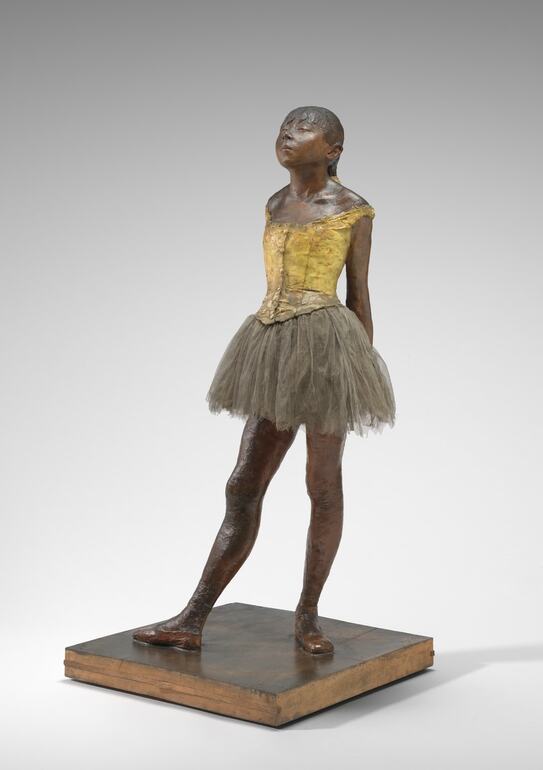
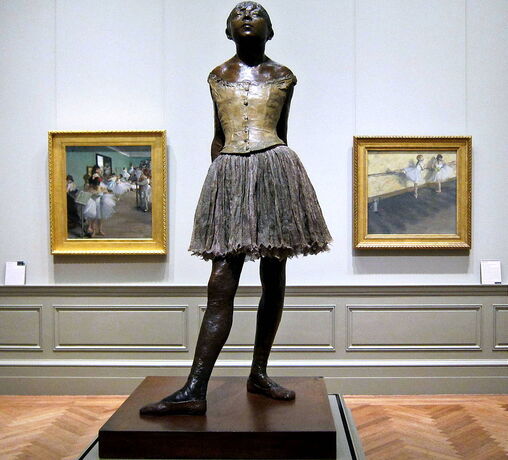
What do you see? A young dancer of fourteen years old is shown at 70 percent of her real size (the sculpture is a bit taller than 3 foot or about 1 meter). She seems relaxed and is standing in ballet’s fourth position (there are seven positions for the feet in ballet, and the ballerina here has her feet in open fourth position – about 12 inches apart and facing different directions). The girl is sculpted realistically and Degas intends to show the hard life of a ballet dancer and what it does to her body. Her back leg supports most of her weight. She has thin legs and arms, holds her arms behind her back, and has her hands clasped together. She confidently holds up her chin, pushes her shoulders back, and her eyes are half closed. She wears ballet shoes, a real tutu made of tarlatan, and a gold-colored bodice (a vest) made of linen. The girl also wears a real ribbon in her plaited hair. Degas used real hair for this sculpture, which he covered in wax.
Copies: The National Gallery of Art holds two statues (the original wax statue and a bronze casting) of the Little Dancer Aged Fourteen as well as two nude studies for this statue. When Degas died, about 150 statues were found in his studio of which only one of the versions in the National Gallery of Art had been shown to the public at an exhibition. Many of these statues were in bad shape, but about half of these statues were repaired after his death. The National Gallery of Art has many of these original statues.
The surviving family of Degas decided to create about 22 bronze casts of these statues. Because of this, nowadays, bronze copies of the Little Dancer Aged Fourteen can be found in many other locations besides the ones mentioned on the top. For example, the statue is also in the the Art Institute of Chicago, Harvard Art Museums, Metropolitan Museum of Art (currently not on view), and the Norton Simon Museum. One of the bronze copies of the Little Dancer Aged Fourteen was sold in 2009 for $19 million.
Who is Degas? Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas (1834-1917) was born in Paris. Whereas he spent most of his life in Paris, he also lived for three years in Italy and spent time in Florence, Naples, and Rome. He started as a more traditional painter by creating historical stories and portraits, but during the 1860s he changed his style and became one of the founders of Impressionism, together with artists like Cézanne, Manet, Monet, Pissarro, and Renoir.
Later on, he changed his focus and started to paint scenes from everyday life with a particular interest in dancers, theater, and horse racing. He moved on to focus on more realistic paintings, and one such example is Interior in the Philadelphia Museum of Art. He made statues mainly as training to understand the anatomy and movements of people.
Fun fact: When Degas showed this sculpture at an Impressionist exhibition in Paris in 1881, many people did not like it at all. For example, some people called the sculpture a monkey. It also did not help that the sculpture was on display in a glass vitrine. Sculptures typically were idealized versions of well-known people created in marble. Instead, Degas created an unknown young girl from Paris, and the girl did not look at all like a goddess. On top of that, he created this sculpture from beeswax and he added objects like a tutu to the statue. Because of the negative reactions Degas got, he removed the statue from the exhibition and stored it in his studio until his death.
Interested in a copy for yourself? Canvas or statue (Amazon links).
Four Stages in Cézanne's Career: This post is part of a series of four providing an overview of the development and change in Paul Cézanne’s approach to his landscapes from the 1860s to the early 1900s. Each part is concerned with a time period of approximately 10–12 years. Scholars have recognized each section and have named them for convenience of recognition.
Where? Musée d'Orsay
When? 1873 Medium and Size? Oil on canvas, 55 x 66 cm. What do you see? This painting is from the years Cézanne spent with the artists who would become known as the Impressionists. In the foreground, a right fork in the road leads steeply down a half-hidden pathway toward a large house with an attached outbuilding. On the right side of the painting is a bank that blends into a thatch roof attached to another building that could be part of the larger house or another house itself. The left fork in the road leads up the hill towards a group of trees in full leaf that bend to the right. The large house in the middle is partially hidden by tall, straight, leafless poplar trees. The construction of the center provides depth and distancing as the rooftops of the village houses lead further into the scene. Beyond the roofs and chimney tops, the green gardens or fields lead to more houses and the hilltop in the right center. The blue sky sets the tone for the whole painting. It feels monochromatic, but the painting is actually full of color. The white on the side of the house, the chimney in the distance, and the rooftops invite the eye further and deeper into the scene. On close examination, the blue of the sky can be seen throughout the painting and is reflected tonally in the rocks, the thatch, the village buildings, and the doorways and windows, as the blue blends, complimenting and connecting each section of the artwork.
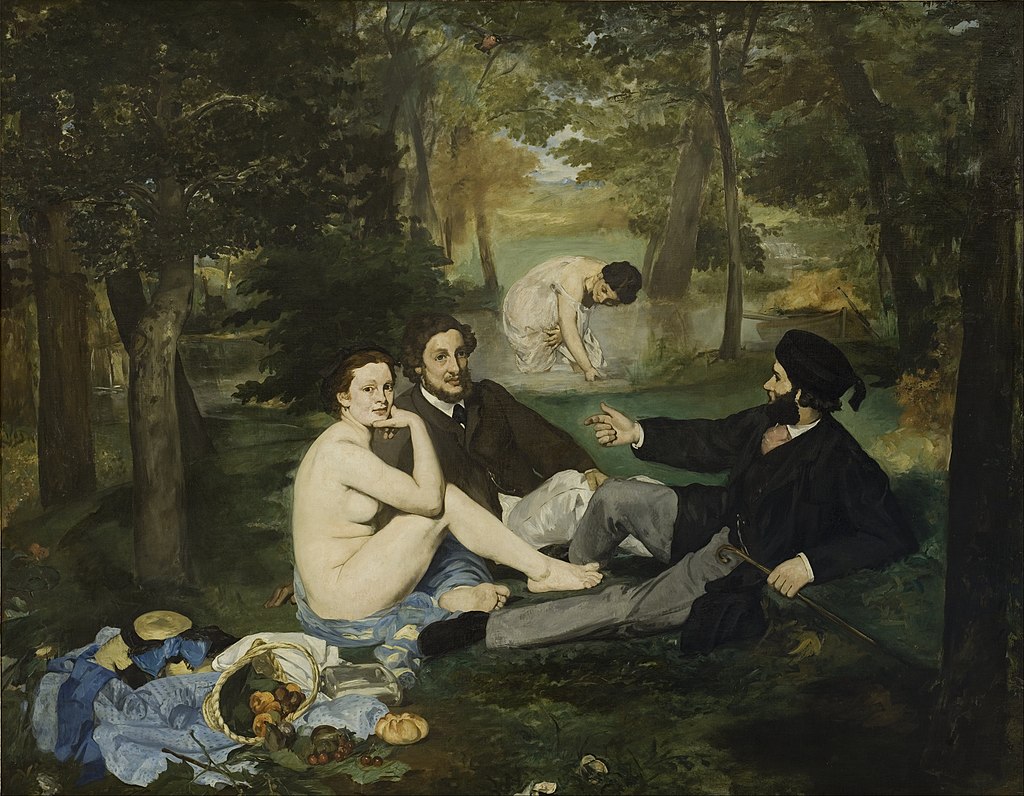
Where? Room 29 on the fifth floor of the Musée d’Orsay
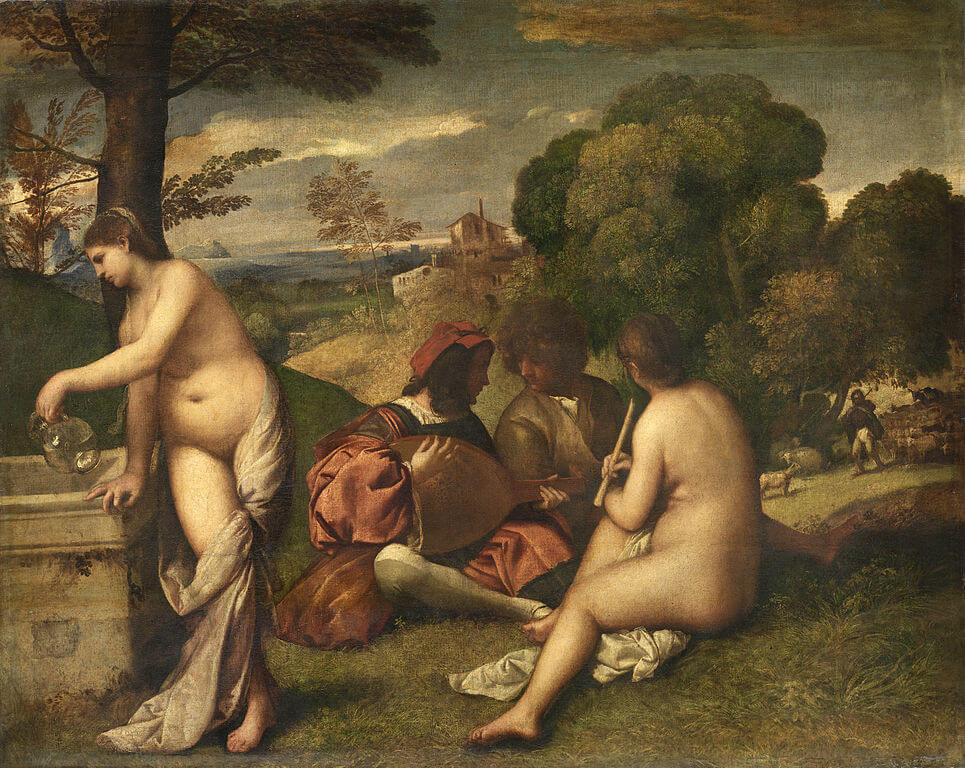
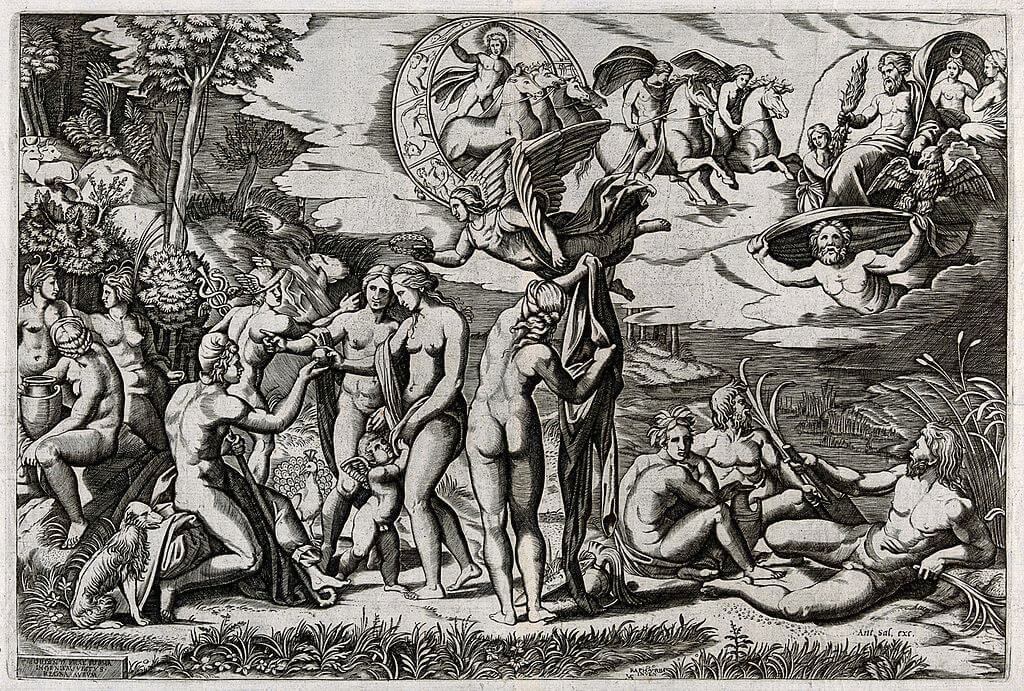
When? 1863 What do you see? Four figures picnicking on the grass. The two men are dressed in fashionable clothes of the 1860s. The man on the right gestures towards the man in the center who seems to be looking elsewhere. Sitting with them is a nude woman. She looks directly at the viewer with her hand on her chin. Her body is minimally shaded, making her appear flat to the canvas. In the lower left corner are the woman’s clothes and a basket of fruit and bread. Behind them, a woman dressed in white is wading in a small body of water. She seems to be reaching for something in the water. A black and orange bird flies over her. On the right is a wooden rowboat. Given her position in the background, this woman is painted larger than you would expect based on the laws of perspective; she isn’t much smaller than the figures in the foreground, creating a confusing sense of depth in the painting. Backstory: Also known as Le Déjeuner sur l’Herbe, the Luncheon on the Grass was inspired by two famous artworks: The Pastoral Concert by Giorgione and/or Titian in the Louvre and a drawing of the Judgement of Paris by Raphael (of which an engraving by Marcantonio Raimondi in the Metropolitan Museum of Art has survived). Despite his knowledge of the old masters, Manet’s work was completely avant-grade and shocking to the Parisian public. Firstly, it was considered offensive to depict a nude woman, especially if the woman was not a goddess or other mythological character. Manet depicts an average woman, breaking the tradition of idealized female nudes like the Venus of Urbino by Titian or The Birth of Venus by Botticelli. Placing her in a contemporary setting with two trendy Parisian men made for a very shocking and offensive scene. Secondly, Manet received a lot of criticism for his painting technique, which featured loose brushstrokes, a departure from the refined finish that can be seen in Renaissance paintings. Thirdly, his rendering of space in this painting is distorted as the woman in the water is abnormally large for her position in the background. For all these reasons, Luncheon on the Grass was rejected from the Paris Salon. Instead, it was exhibited at the Salon des Refusés in 1863. There, it was still received with ridicule and outrage for its subject matter and technique. People laughed at the painting and some even hit the painting with sticks. Critic Louis Etienne called it a “young man’s practical joke” and a “shameful open sore” in Le Jury et les Exposants.
Who is Édouard Manet? Édouard Manet was born in 1832 in Paris where he died 51 years later. Manet was a Parisian Realist painter who studied under Thomas Couture for six years. Afterward, however, he decided against attending the École des Beaux-Arts.
Early on in his career, he befriended Charles Baudelaire whose work featured urban outsiders such as prostitutes and street entertainers. Baudelaire’s writing inspired Manet to continue painting unusual characters alongside his other works that featured better-known figures such as musicians and writers. Manet’s avant-garde style that preceded Impressionism was often attacked by the press, but he was also defended by other creatives such as Emile Zola, Claude Monet, and Pierre-Auguste Renoir. Among his famous paintings are Olympia in the Musée d’Orsay (and painted in the same year as the Luncheon on the Grass) and The Battle of the Kearsarge and the Alabama in the Philadelphia Museum of Art.
Fun fact: The nude woman in Luncheon on the Grass is modeled after Victorine Meurent who also posed for Manet’s Olympia. She was a working class woman and aspiring painter whose work was actually exhibited in the Paris Salon of 1876. She and Manet had a close relationship, but her willingness to pose nude for his paintings tarnished her reputation. The men in the painting were modeled after Gustave Manet and Ferdinand Leenhoff, Manet’s brother and brother-in-law. respectively.
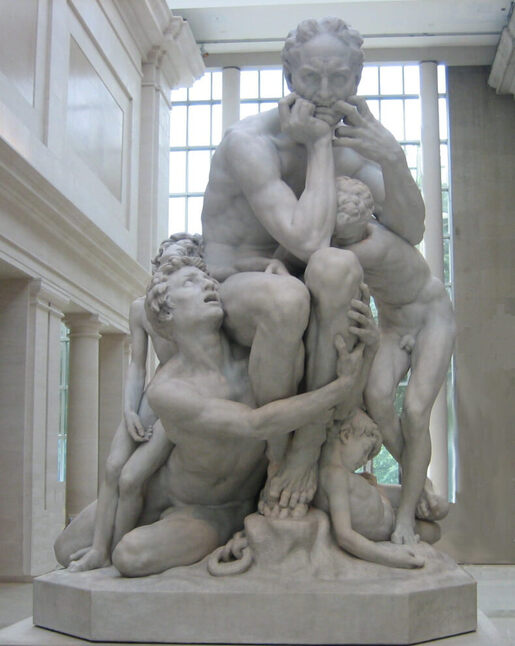
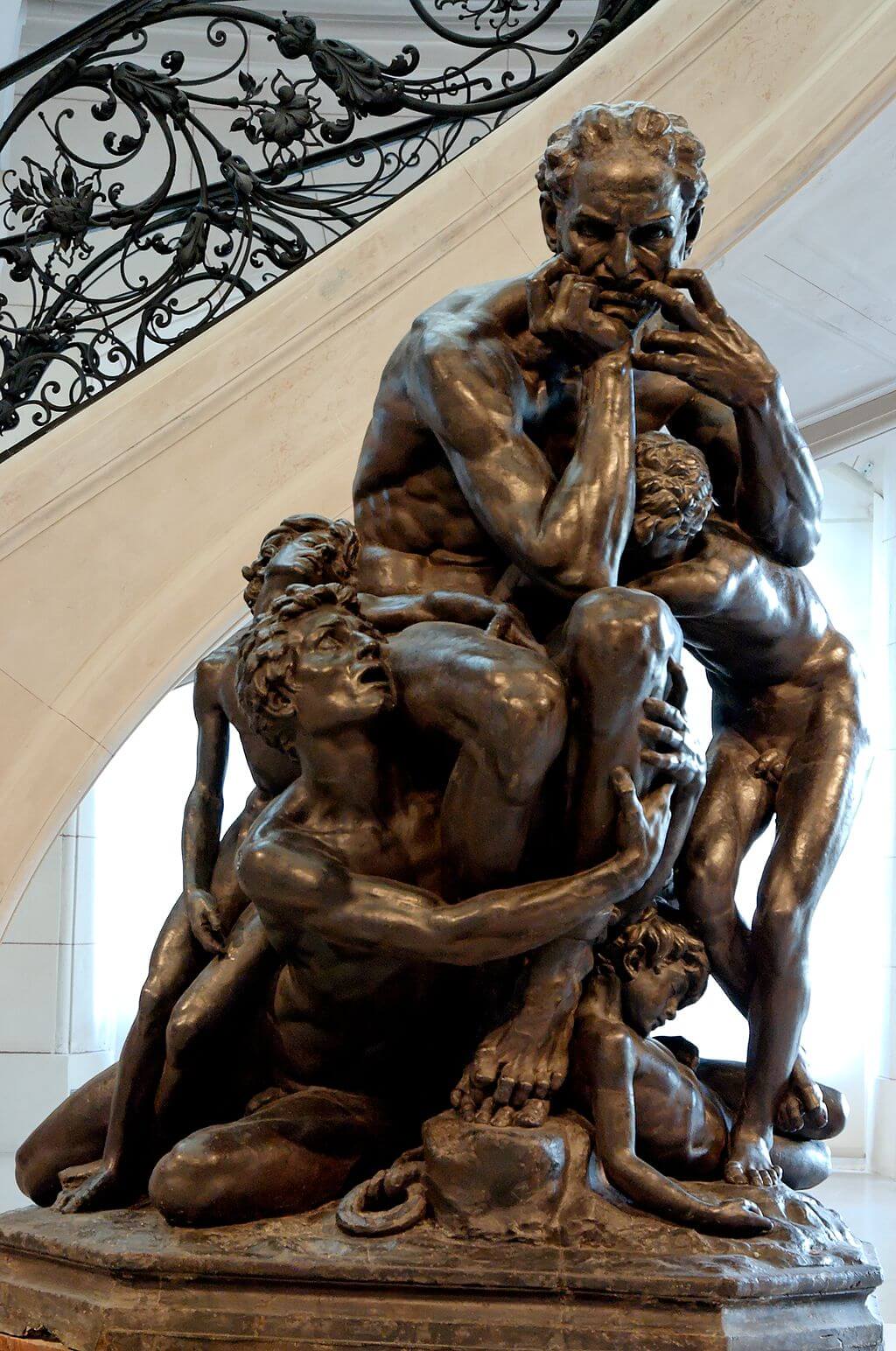
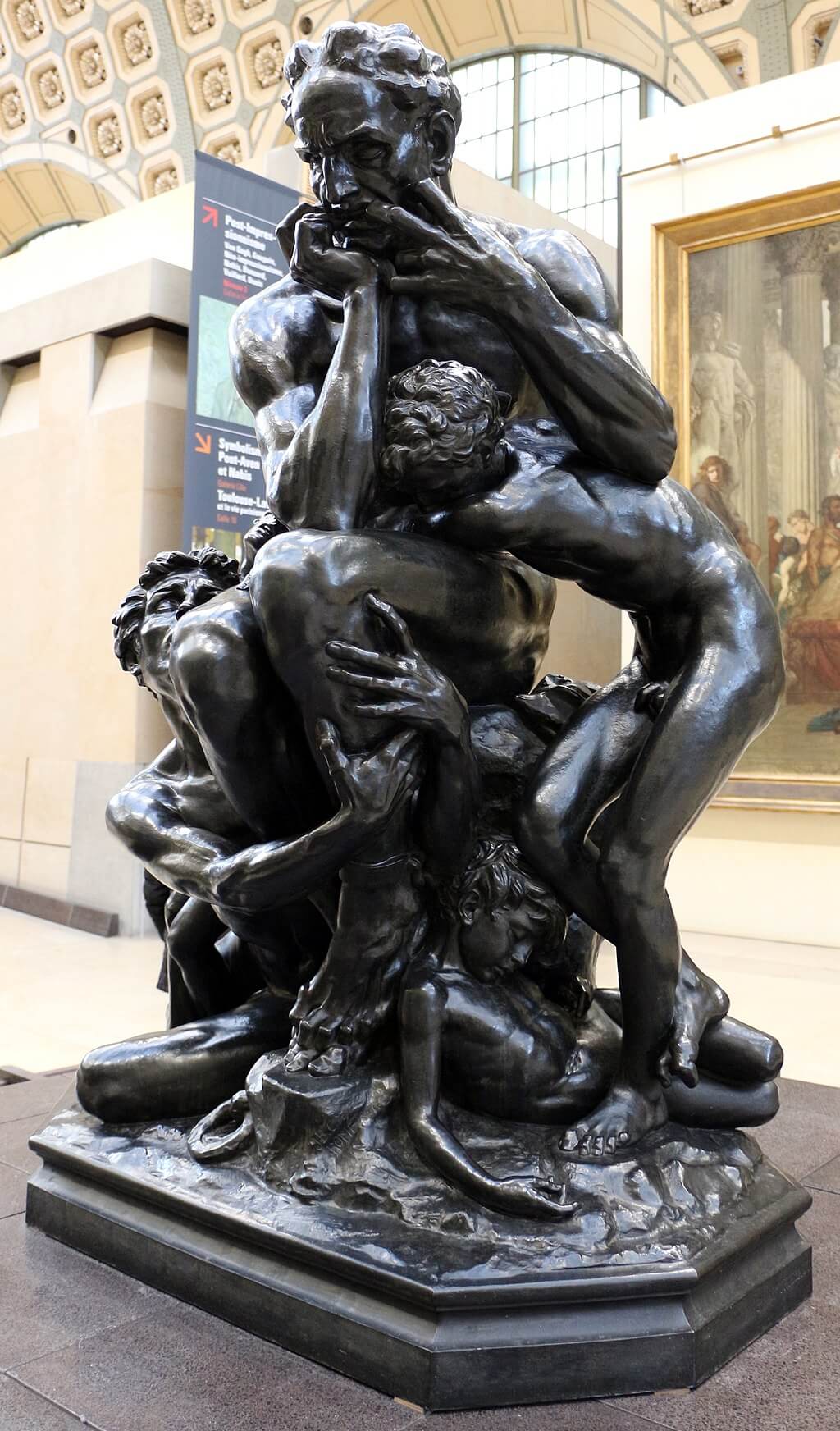
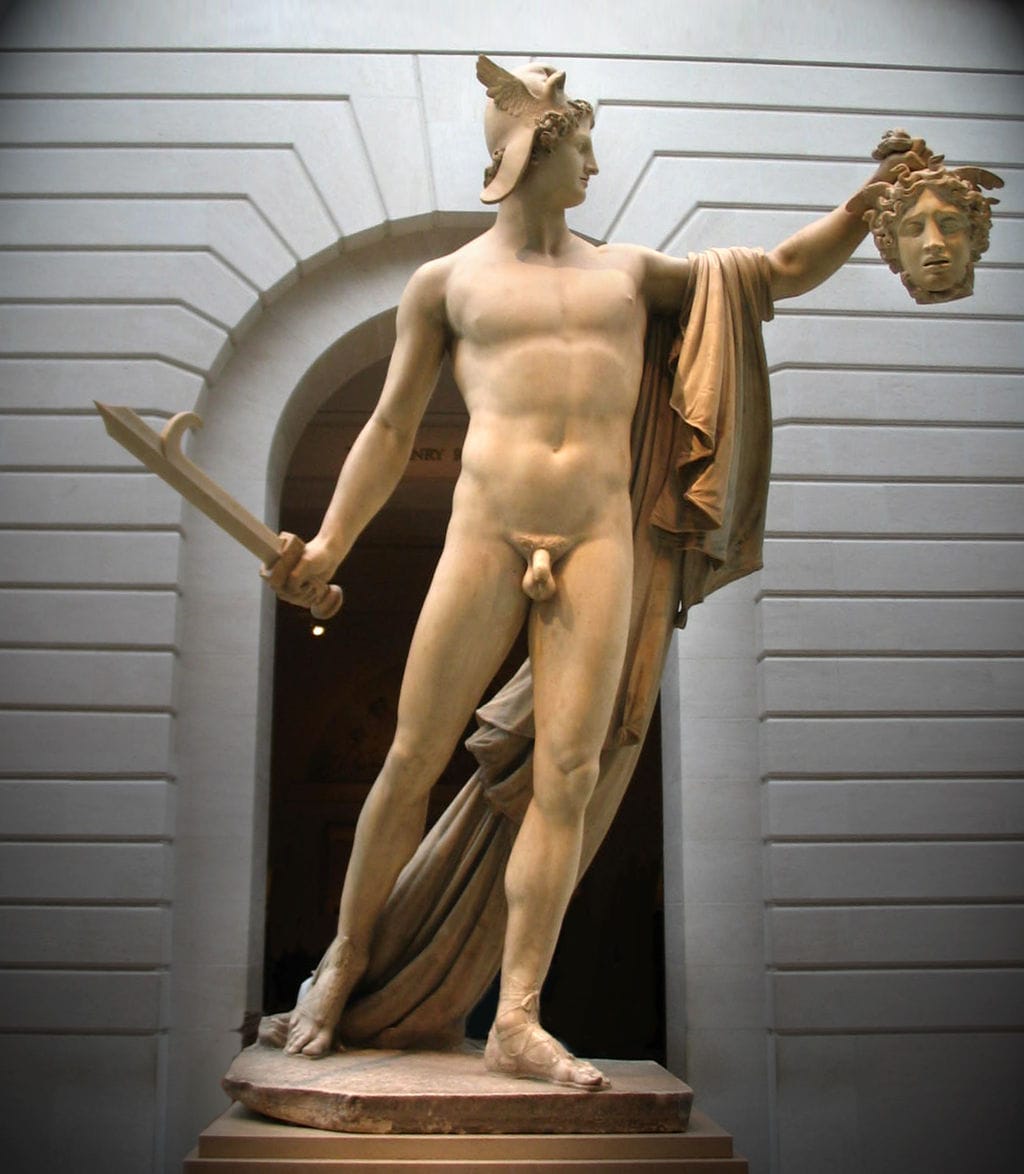
Where?
What do you see? Ugolino is sentenced to starve to death together with his children. This sculpture shows the moment that Ugolino considers cannibalism. He is depicted together with his four children, all naked, but is ignoring his children in this sculpture. He looks desperately in the distance and is biting his fingers and pulls his lip down with them. He holds his head in the palm of his hand. He is contemplating the consequences of his sins. He is sculpted as a muscular man even though he is starving to death. He is bending forward and has his feet on top of each other. The four children are in different states of suffering, and they beg their father to eat them such that he can stay alive. The oldest boy seems most energetic. He has his fingers in the flesh of Ugolino’s leg to emphasize his begging. The second oldest son on the right is also holding his father with both hands. The second youngest son on the left sits on top of his oldest brother and has already lost most of his remaining energy. He has his left arm on his father’s leg. The youngest son is on the bottom right and while he is the only one with a peaceful expression he appears already dead. Carpeaux is telling a story with this sculpture, something that is very difficult to do in a sculpture. He was able to sculpt the skin, muscles, and veins very realistically and to express the strong emotions of the different subjects. The more you look at the details of this marble statue, the more "alive" the subjects become. For example, you can see Ugolino’s agony by the curve in his spine, and even the toes of Ugolino are curled to show his agony. Different versions of this statue: Several sculptures of Ugolino and His Sons have been made. Carpeaux got the idea of creating a sculpture of Ugolino and his sons in 1858. He started by making a plaster version of it, which he completed in 1861. This version is in the Petit Palais in Paris. After that, in 1862, he created a bronze version which is now in the Musée d’Orsay. The final version he created was the marble version in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Rodin was inspired by the sculptures of Carpeaux and, in 1881, he made a plaster version of Ugolino and His Children which is in the Musée Rodin in Paris.
Backstory: This work is created under the supervision of Carpeaux and is based on canto 33 of Dante’s Inferno (which is the first part of the Divine Comedy). In this book, Dante travels through the nine circles of hell. Each circle contains people who are convicted in hell for a different sin. In the ninth circle, he meets Count Ugolino della Gherardesca (c. 1220-1289), who was convicted for treachery. In 1288, Ugolino worked together with the archbishop Ruggieri to take control of the factions in Pisa. However, in this process, Ruggieri betrayed him and locked Ugolino up in prison.
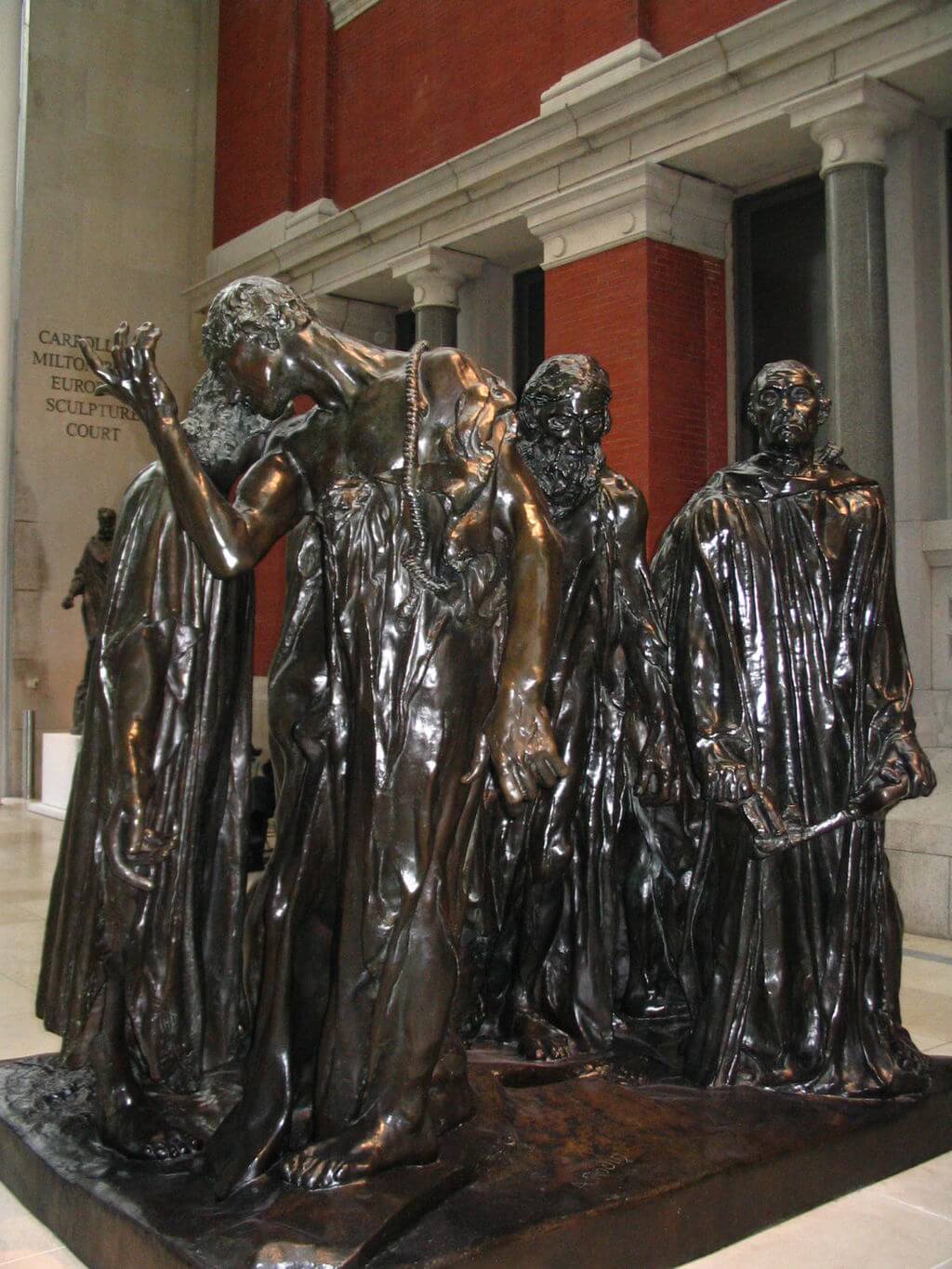
More precisely, Ugolino was imprisoned together with his children and grandchildren in a tower and condemned to starve to death. His children begged Ugolino to eat them to survive, and his hunger was stronger than his sadness about his dying children. It is unclear whether Ugolino ate his children in the end. In Dante’s story, Ugolino’s eternal punishment in hell is that he is stuck up to his head in the icy waste of Antenora which is the punishment for political traitors. Meanwhile, he is chewing the head of Ruggieri (the person who betrayed him in real life) who is also stuck in the ice. Who is Carpeaux? Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux (1827-1875) was born in Valenciennes, France and died in Paris. In 1854, he moved to Rome, where he got inspired by the Renaissance artists such as Donatello, Michelangelo, and Del Verrocchio. Carpeaux suffered a lot during his life, both mentally and physically, and you can see that back in some of his extreme works. His sculptures are known for the emotions they evoked among the viewers, and he distinguished himself with his style from his contemporary colleagues. He is considered one of the greatest sculptors of his time, though most people consider Antonio Canova (who was born before him) and Auguste Rodin (who was born after him) to be even better. Fun fact: The sculpture in the Metropolitan Museum of Art is placed very close to the entrance of the Petrie Court Café. It is ironic that this sculpture with the theme of starvation is so close to the Café. While this may be a coincidence in itself, another statue that deals with starvation is also close to the Café. Rodin’s bronze The Burghers of Calais sculpture shows six leaders of the city of Calais who are starving and have a rope around their neck as they will be executed soon. The marble statue of Carpeaux is also next to the statue of Perseus with the Head of Medusa by Antonio Canova.
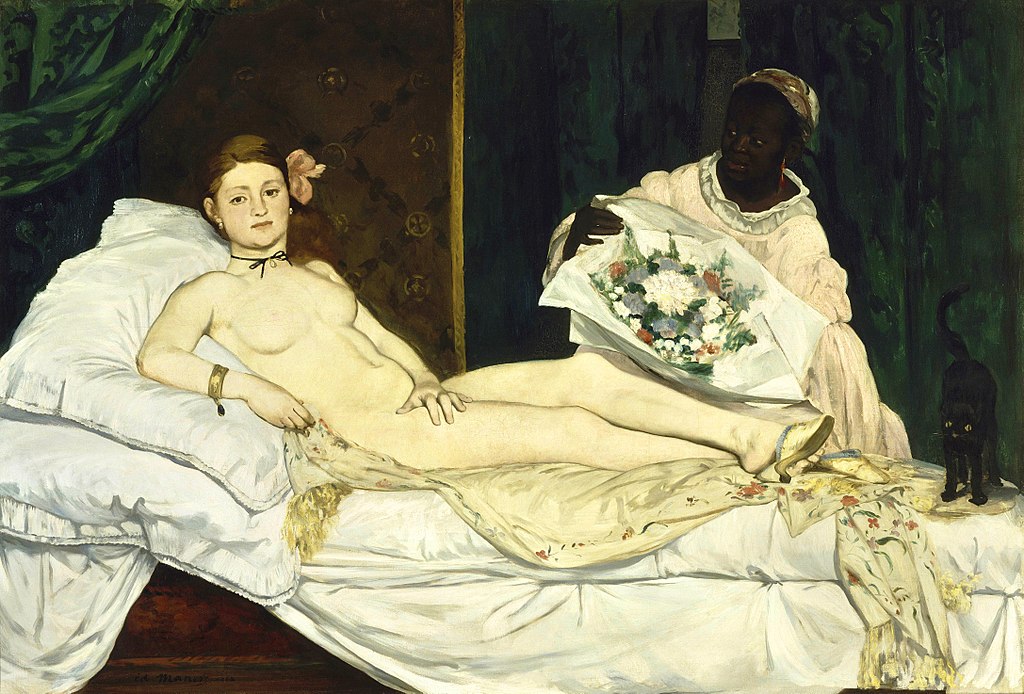
Where? Room 14 on the Ground floor of the Musée d’Orsay
When? 1863 What do you see? A Parisian prostitute, Olympia, lies down on her bed in her apartment. She rests atop a floral cloth, staring directly at the viewer as her servant presents her with a bouquet (perhaps a gift from an admirer or patron). Olympia’s left hand is firmly placed over her private area. She is pale, and her features are not idealized as was typically done by other artists at this time. Instead, Manet painted her realistically. Olympia’s body has dark outlines and broad color that lacks shading. She appears flat and stands in stark contrast to the dark brown and green background behind her. At her feet is a startled black cat with its tail raised. Backstory: Victorine Meurent served as the model for Olympia. She was a painter herself and served as a model for various artists. Manet liked her as a model because of her petite stature and red hair. Laure served as the model for the maid, and she posed for several other paintings of Manet. Édouard Manet got his inspiration for Olympia from the Venus of Urbino, the iconic Renaissance painting by Titian in the Uffizi Museum. Titian’s painting is a classic example of the female nude as a manifestation of ideal beauty. His reclining nude, like most, was shrouded in perfection and mythology. It was not inherently sexual. In his painting, Manet reduced the female nude to a much more realistic form. There is no beauty or goddess to admire; the viewer is confronted with Olympia’s sexuality as well as the reality of prostitution in Paris. And unlike the demure and reserved reclining nudes of the past, Manet’s modernized version features a woman who addresses the viewer and holds a firm posture.
Controversy: The painting caused quite an uproar when it was displayed in the Paris Salon in 1865. The French public was not ready to receive such a bold painting that deviated so strongly from what they were used to. Over seventy critics condemned the work for a variety of reasons and political cartoons mocking Olympia as ugly surfaced in newspapers and magazines.
The realistic style of this painting was not appreciated. Moreover, to show a sex worker as so bold and independent was very unconventional during the time. The idea that Olympia could live so comfortably (with flowers and jewelry) shook critics to the core. In addition, the painting breaks tradition by showing an imperfect female nude who stands in contrast to the flawless depictions of Venus from the past. Who is Olympia? In 1860s France, “Olympia” was an alias commonly used by prostitutes or courtesans. She is not of lower status as we would expect. Instead, she is shown to be of a higher class, adorned with jewelry and resting on a floral blanket with a servant at her side. Who is Manet? Édouard Manet was born in 1832 in Paris where he died 51 years later. He was a Parisian realist painter who studied in the studio of Thomas Couture for six years. Afterward, however, Manet decided against attending the official art school of the French Academy, the École des Beaux-Arts. Early on in his career, he befriended the poet Charles Baudelaire whose work featured urban outsiders such as prostitutes and street entertainers. Baudelaire’s writing inspired Manet to continue painting unusual characters alongside his other works that featured better-known figures such as musicians and writers. Manet also had a love for the sea and occasionally liked to capture this in this works, such as the Battle of the Kearsarge and the Alabama in the Philadelphia Museum of Art. While most of Manet’s works can be classified under Realism, he is also one of the masterminds behind the development of Impressionism. The Rue Mosnier with Flags in the Getty Museum is a good example of his Impressionist ideas.
Fun fact: In 1867, Manet held a solo exhibition during the World’s Fair in Paris. Once again, Olympia was on display. When the painting received criticisms once again, writer Emile Zola defended it with a pamphlet that praised Manet’s bold style and technique. He asked viewers to overlook the subject matter and appreciate Manet’s avant-garde approach to art. As thanks, Manet produced the Portrait of Emile Zola. It features Zola in his study, reading some of his own works. In the upper right, Manet added a miniature print of Olympia to Zola’s wall.
Where? Room 31 of the Musée d'Orsay
When? 1876 What do you see? An open-air dance in Montmartre (a hill and district in Paris). On the table in the foreground sits a 16-year old model in a striped dress. Her name is Estelle. Probably, her older sister, Jeanne Samary, stands behind her and is in conversation with the painter Franc Lamy. Renoir used Jeanne Samary more often as a model for his paintings, such as in The Swing which is also in the Musée d’Orsay. The man on the right side of the other side of the table is George Rivière, the biographer of Renoir, and the man smoking a pipe on the left is the printmaker Norbert Goeneutte. Behind the seated people in the foreground, people are dancing under the acacia trees. The dancing women are mainly local people, and the men are mostly friends of Renoir. On the bottom left, a child is playing with her mother. This painting may be painted on a Sunday afternoon when the dance hall was open to families with children. On the top, we can identify some chandeliers that are hanging in the trees, as well as some lights on a pole on the right.
The effects of light: Renoir paid careful attention to the effect of the sunlight on the dancing people. It seems to be a sunny day, but the trees block part of the sunlight. We can see the brighter and darker areas in the painting by looking at the ground and the colors of the dresses of the woman. Look also at the man sitting with his back toward us in the right foreground. He has some light patches on his jacket and head. This is the result of the sunlight shining through the trees.
Backstory: This painting is also known as ‘Bal du Moulin de la Galette’ and ‘Au Moulin de la Galette.’ Moulin de la Galette was the name of a neighborhood dance hall located next to a windmill (moulin is French for windmill). Renoir also painted a smaller version of this painting which is in a private collection. In that version, he leaves out more details. This painting was sold in 1990 for $78.1 million, which is still a record for a Renoir painting. It is uncertain which of the two versions has been painted first. The current version is in the Musée d’Orsay since 1986 when it was transferred from the Louvre. Renoir used loose brush strokes to paint this work, and the painting lacks quite some detail. On the Impressionist exhibition where this painting was first shown to the public, some people were confused and thought that Renoir did not finish his painting yet. However, Renoir left out many details on purpose as he understood that the human eye could fill in the details when looking at the painting. This allowed him to focus on the effects of light and movement, and create a bright and happy painting of the public dance. Open-air dance halls? The Moulin de la Galette was an open-air dance hall in Paris in the 1870s. Open-air dance halls were very popular in 19th-century France and were a great source of entertainment for the people. Most people went there not to dance, but just to watch the dancers and enjoy the relaxed atmosphere. Renoir is the only Impressionist artist to depict this theme in his paintings. Renoir attended most of the events at the Moulin de la Galette, sometimes accompanied by other artists like Degas, and liked to dance there as well. To watch the dancers at the Moulin de la Galette, you had to pay a quarter French franc. The Moulin de la Galette first opened around 1833. Who is Renoir? Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1841-1919) is a French painter from Limoges in the middle of France. When Pierre-Auguste was three years old, his family moved to Paris where they lived close to the Louvre. It was a dream of him to have his work on display in the Louvre and in the last year of his life, he visited the Louvre where he could see his own work hanging among the masterpieces that he admired as a child. Renoir is one of the founders of Impressionism, together with artists like Cézanne, Degas, Manet, and Monet. The Impressionists focused on the effects of light and often painted outside. Renoir’s opinion about art was that it should be pretty and he mostly painted very happy scenes. Two good examples are The Apple Seller in the Cleveland Museum of Art and A Girl with a Watering Can in the National Gallery of Art.
Fun fact: Renoir painted an open-air dance in Montmartre, a neighborhood in Paris that was popular among artists in the second half of the 19th century. It was the home to artists like Degas, Manet, Monet, Picasso, and Van Gogh. Renoir lived there as well and rented a studio close to the dance hall depicted in this painting. He brought the canvas from his studio to the dance hall to paint the dance. Many people that he knew participated in the dance. The story goes that, on some days, when it was windy, some of his friends there had to help him to keep the canvas straight while he was painting.
Interested in a copy for yourself? Poster or canvas
Where? Room 14 of the Musée d’Orsay
When? 1868 What do you see? The 27-year old writer Émile Zola sits straight in a cushioned chair. He is fashionably dressed as a Parisian dandy, wearing a black jacket with grey pants. One hand rests on his knee, half-clenched. In his other hand, he holds Charles Blanc’s L’Histoire des Peintres, a book about art history. Zola seems to be in thought about something he has just read. The blankness of his expression makes the objects around him the subject of the viewer’s attention. In the background are artifacts from Japan, including an ink well on the desk, a painted screen on the far left, and a print of Utagawa Kuniaki’s Wrestler of Onaruto Nadaemon on the wall. The organized clutter atop his desk accentuates his wit and intellect. Among the books is a light blue pamphlet in which Zola defended Manet controversial painting Olympia. Directly above it is a print of Olympia herself. Behind it is a print of another famous painting, The Triumph of Bacchus by Diego Velázquez.
Backstory: In 1867, Manet had a solo exhibition. His best-known work, Olympia, was put on display for the second time. The work had received much criticism in 1865 for its avant-garde subject matter and “unrefined” style. Upon its second public display, the painting was once again the subject of many harsh comments.
Writer Émile Zola came to Manet’s defense and wrote an article in La Revue du XXe siècle. The article praised Manet’s bold style and technique, asking viewers to overlook the “risque” subject matter. Zola later published the article in its own brochure that sits on his desk in this portrait. As thanks, Manet painted Zola’s portrait. Over the course of several months, Zola posed extensively for the portrait in Manet’s studio. According to Zola, these sessions were long and exhausting as Manet did not engage in much conversation when he was painting. Manet’s main emphases in this portrait were Zola’s intellect and the aesthetics of the Far East. With the influx of Japanese goods into France in the mid-nineteenth century, many artists began imitating the flatness and simplicity of Japanese woodblock prints. This movement, known as Japonisme, was a precursor to Impressionism. Who is Émile Zola? A French writer who was born in 1840 in Paris. He is often credited as a founder of the naturalism movement in literature. He was childhood friends with Paul Cézanne who later introduced him to Manet. Zola was unemployed and lived in poverty for two years of his adult life. It was only when he published his first novel, Claude’s Confession that he was able to land a job as a journalist. Zola went on to write many more novels and published his best-known series, The Rougon Family Fortune. In the 1860s, Zola defended Impressionist artists like Cézanne, Manet, Renoir, and Monet. Who is Manet? Édouard Manet was born in 1832 in Paris where he died 51 years later. He was a Parisian Realist painter who studied in the studio of Thomas Couture for six years. Afterward, however, Manet decided against attending the official art school of the French Academy, the École des Beaux-Arts. Early on in his career, he befriended the poet Charles Baudelaire whose work featured urban outsiders such as prostitutes and street entertainers. Baudelaire’s writing inspired Manet to continue painting unusual characters alongside his other works that featured better-known figures such as musicians and writers. Manet was friends with Monet who he first considered to be a rival. He believed Monet to be copying his work. However, the pair made amends and eventually traveled to Argenteuil together. Many works came out of this trip, including Monet Painting in his Studio Boat.
Fun fact: Manet altered the print of Olympia in his portrait for Zola. Instead of facing the viewer, Olympia is looking at Émile Zola who had publicly defended her after this painting had received so much criticism at the Paris Salon (a very popular yearly art exhibition) of 1865.
Three years later, Manet submitted the painting to the Paris Salon of 1868 where it got accepted. The painting received mixed critical reviews. Some thought that the portrait was one of the best at the Salon of that year, while others thought the painting lacked animation and that it looked more like a still life than a portrait. |
Categories
All
|
- Home
- Blog
-
Museums
- Alte Pinakothek
- Art Institute of Chicago
- Baltimore Museum of Art
- Barber Institute of Fine Arts
- Bargello
- Barnes Foundation
- British Museum
- Church of Sant’Anastasia
- Cleveland Museum of Art
- Courtauld Institute of Art
- Detroit Institute of Arts
- Frans Hals Museum
- Galleria Borghese
- Gallerie dell'Accademia
- Getty Museum
- Guggenheim
- Hermitage Museum
- Kunsthistorisches Museum
- Kunstmuseum Basel
- Legion of Honor Museum
- Louvre
- Mauritshuis
- Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Musee d’Orsay
- Museum of Fine Arts in Boston
- Museum of Modern Art
- National Gallery in London
- National Gallery of Art
- National Museum in Poznań
- Norton Simon Museum
- Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek
- Palace of Versailles
- Palazzo Pitti
- Palazzo Vecchio
- Petit Palais
- Philadelphia Museum of Art
- Prado
- Pushkin Museum
- Ravenna Art Museum
- Rijksmuseum
- San Diego Museum of Art
- Santa Maria delle Grazie
- St. Peter's Basilica
- Städel Museum
- Statens Museum for Kunst
- Tate Britain
- Tate Modern
- Timken Museum of Art
- Uffizi
- Vatican Museums
- Wallace Collection
-
Artists
- Altdorfer
- Anguissola
- Berlin Painter
- Bosch
- Botticelli
- Boucher
- Bronzino
- Bruegel the Elder
- Brunelleschi
- Cabanel
- Caillebotte
- Canova
- Caravaggio
- Carpeaux
- Cezanne
- Cimabue
- David
- Degas
- Delacroix
- De Maria
- Donatello
- El Greco
- Fontana
- Fra Angelico
- Fragonard
- Gauguin
- Gentileschi
- Gericault
- Gonzalez-Torres
- Goya
- Hals
- Hogarth
- Hokusai
- Ingres
- Leonardo da Vinci
- Lippi, Filippo
- Longhi, Barbara
- Lorrain
- Makovsky
- Manet
- Massys
- Matisse
- Merian
- Michelangelo
- Mochi
- Modigliani
- Monet
- Panini
- Parmigianino
- Perugino
- Picasso
- Pisanello
- Raphael
- Rembrandt
- Renoir
- Reynolds
- Rivera
- Rodin
- Rubens
- Scultori
- Seurat
- Steen
- Tintoretto
- Titian
- Toulouse-Lautrec
- Turner
- Uccello
- Van der Weyden
- Van Dyck
- Van Eyck
- Van Gogh
- Van Hemessen
- Vasari
- Velazquez
- Vermeer
- Veronese
- Vigée Le Brun
-
Locations
- Books
- About Us