|
Where? Room 58 of the National Gallery
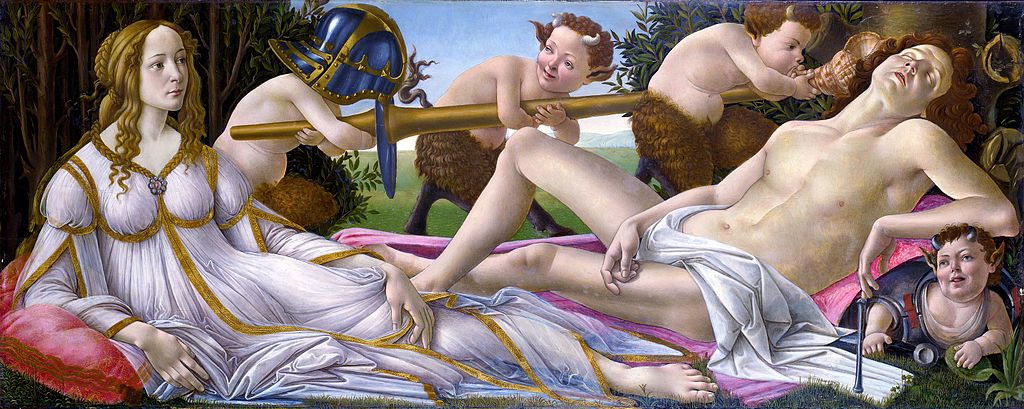
When? 1482-1485 What do you see? On the left, you see the goddess Venus who is carefully watching the god Mars on the right, who is asleep. Venus and Mars are having an adulterous affair. Uncharacteristically, Mars is unarmed, and he lies on a red cloak. You can also see four fauns (mythological figures who are half human and half goat, have small horns and tails, and they are followers of Bacchus). The fauns are blowing a Triton’s shell (a hunting horn in ancient times) like a trumpet in the ear of Mars to show that after making love even this very loud sound will not wake him up. They are also jokingly playing with the weapon of Mars (a lance), his body armor (to be precise, a cuirass; see the faun on the bottom right) and his helmet (the faun on the left). Venus is wearing a beautiful dress. On the top right you can see a swarm of wasps. Also, if you look carefully, you can see the city of Florence in the distance. Backstory: This painting is both inspired by Greek mythology and a description of the Greek writer Lucian of Samosata (125-180) of a lost painting on Alexander the Great and his wife, Roxana. According to the mythological stories, Venus is still married to the blacksmith Vulcan (the god of fire) when she is having an affair with Mars. Whenever Venus was having an affair, Vulcan would get so angry that he treated the metal with such force that it created a volcanic eruption. Based on the dimensions of the painting (27 x 69 inches – 69 x 174cm), this painting was likely meant to be a decoration for the backboard of a bed or a storage box. The National Gallery acquired the painting around 1874 for £1,050. Symbolism: The overall message of this painting is that love trumps war. Venus (the goddess of love) is awake, while her lover Mars (the god of war) is asleep. On the top right, you can see a swarm of wasps, which represent the stings of love. They may also refer to the Vespucci family (vespa is Italian for wasp). Simonetta Vespucci was a beautiful woman who most likely served as the model for this painting, and she was the inspiration for many of Botticelli’s paintings. The myrtle trees behind Venus are one of the main symbols of Venus as myrtles are known as a potent aphrodisiac. Who is Botticelli? Sandro Botticelli (1445-1510) was a painter who belonged to the Florentine school of painters. Botticelli was initially trained by his brother to become a goldsmith, but at the age of 14, he became an apprentice to the successful painter Filippo Lippi (1406-1469), known from the painting Madonna and Child with Two Angels. Greek mythological stories often inspired Botticelli’s work, and he used Venus more often as a topic for his work. For example, Venus was also the center of attention in his famous paintings The Birth of Venus and La Primavera, both in the Uffizi Museum. Botticelli was in love with Simonetta Vespucci (a cousin-in-law of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci), who was already married to someone else. Simonetta was known as the greatest beauty of her time and died in 1476. As a result, Botticelli never married. Throughout his life, he has been inspired by Simonetta, who has served, according to popular belief, as the inspiration for many of his paintings (including the current one). According to his wish, Botticelli was buried at the feet of Simonetta Vespucci.
Who are Venus and Mars? Venus is the Roman goddess of love, beauty, sex, fertility, prosperity, and desire. Venus is also known in the Greek mythology as Aphrodite. In Latin the noun Venus means ‘sexual desire’. Julius Caesar claimed to be an ancestor of Venus.
Mars, the god of war, is one of the lovers of Venus. Mars is also an agricultural guardian. The Greek counterpart of Mars is Ares. The third month of the year, March, is named after him. In many mythological stories, Cupid is portrayed as the son of Venus and Mars.
Written by Eelco Kappe
References:
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
All
|
- Home
- Blog
-
Museums
- Alte Pinakothek
- Art Institute of Chicago
- Baltimore Museum of Art
- Barber Institute of Fine Arts
- Bargello
- Barnes Foundation
- British Museum
- Church of Sant’Anastasia
- Cleveland Museum of Art
- Courtauld Institute of Art
- Detroit Institute of Arts
- Frans Hals Museum
- Galleria Borghese
- Gallerie dell'Accademia
- Getty Museum
- Guggenheim
- Hermitage Museum
- Kunsthistorisches Museum
- Kunstmuseum Basel
- Legion of Honor Museum
- Louvre
- Mauritshuis
- Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Musee d’Orsay
- Museum of Fine Arts in Boston
- Museum of Modern Art
- National Gallery in London
- National Gallery of Art
- National Museum in Poznań
- Norton Simon Museum
- Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek
- Palace of Versailles
- Palazzo Pitti
- Palazzo Vecchio
- Petit Palais
- Philadelphia Museum of Art
- Prado
- Pushkin Museum
- Ravenna Art Museum
- Rijksmuseum
- San Diego Museum of Art
- Santa Maria delle Grazie
- St. Peter's Basilica
- Städel Museum
- Statens Museum for Kunst
- Tate Britain
- Tate Modern
- Timken Museum of Art
- Uffizi
- Vatican Museums
- Wallace Collection
-
Artists
- Altdorfer
- Anguissola
- Berlin Painter
- Bosch
- Botticelli
- Boucher
- Bronzino
- Bruegel the Elder
- Brunelleschi
- Cabanel
- Caillebotte
- Canova
- Caravaggio
- Carpeaux
- Cezanne
- Cimabue
- David
- Degas
- Delacroix
- De Maria
- Donatello
- El Greco
- Fontana
- Fra Angelico
- Fragonard
- Gauguin
- Gentileschi
- Gericault
- Gonzalez-Torres
- Goya
- Hals
- Hogarth
- Hokusai
- Ingres
- Leonardo da Vinci
- Lippi, Filippo
- Longhi, Barbara
- Lorrain
- Makovsky
- Manet
- Massys
- Matisse
- Merian
- Michelangelo
- Mochi
- Modigliani
- Monet
- Panini
- Parmigianino
- Perugino
- Picasso
- Pisanello
- Raphael
- Rembrandt
- Renoir
- Reynolds
- Rivera
- Rodin
- Rubens
- Scultori
- Seurat
- Steen
- Tintoretto
- Titian
- Toulouse-Lautrec
- Turner
- Uccello
- Van der Weyden
- Van Dyck
- Van Eyck
- Van Gogh
- Van Hemessen
- Vasari
- Velazquez
- Vermeer
- Veronese
- Vigée Le Brun
-
Locations
- Books
- About Us